Introduction to Medical Syringes
Medical syringes have a storied history that dates back to ancient times. Early forms of syringes were rudimentary, often fashioned from hollow reeds or animal bladders. These early tools laid the groundwork for the sophisticated medical syringes we use today. The modern syringe, as we recognize it, began to take shape in the 19th century with the advent of Charles Gabriel Pravaz’s and Alexander Wood’s innovations. Their developments led to the creation of the hypodermic syringe, a pivotal advancement in medical technology.
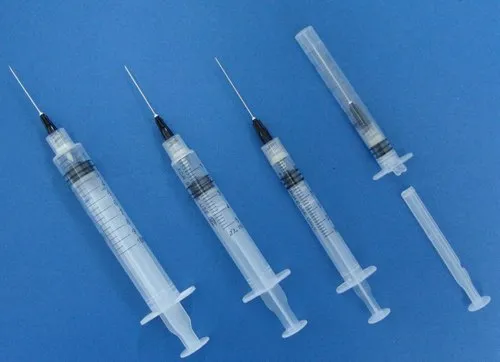
A typical medical syringe comprises three main components: the barrel, the plunger, and the needle. The barrel is a cylindrical tube that holds the liquid medication. It is usually marked with graduated measurements to ensure precise dosing. The plunger fits snugly inside the barrel and is used to draw in and expel the liquid. The needle, attached to the end of the barrel, is the part that penetrates the skin to deliver the medication or draw fluids. Each component is meticulously designed to ensure accuracy, sterility, and ease of use.
Several types of syringes are utilized across various medical settings, each tailored to specific applications. Hypodermic syringes are perhaps the most common, used for injecting medications or drawing blood. Insulin syringes are specifically designed for diabetic patients, featuring finer needles and smaller barrels to accommodate the precise dosing required for insulin administration. Tuberculin syringes, on the other hand, are used primarily for tuberculosis testing and administering small doses of medication or vaccines. These syringes typically have a finer gauge needle and a smaller volume capacity to ensure accurate dosing.
Understanding the history, components, and types of medical syringes provides a solid foundation for appreciating their critical role in healthcare. This knowledge is essential for healthcare professionals and anyone involved in the medical field, ensuring the effective and safe use of these indispensable tools.
Applications and Best Practices for Using Medical Syringes
Medical syringes are indispensable tools in various healthcare settings, serving critical roles in diverse medical procedures. One of the primary applications of medical syringes is the administration of medications. Intravenous, intramuscular, and subcutaneous injections are common methods that utilize syringes to deliver precise doses of medication directly into the bloodstream or muscle tissue, ensuring rapid therapeutic effects. Vaccinations also rely heavily on syringes; they are used to introduce vaccines into the body to stimulate the immune system and provide protection against diseases.
Another crucial application of medical syringes is in the drawing of blood for diagnostic purposes. Phlebotomists and healthcare professionals use syringes to collect blood samples, which are subsequently analyzed to diagnose conditions, monitor health status, and guide treatment decisions. Additionally, syringes are utilized in various medical procedures, including the aspiration of fluids from the body, the delivery of anesthesia, and the administration of contrast agents during imaging studies.
To ensure the efficacy and safety of these procedures, it is vital to select the appropriate syringe type and size. The choice of syringe depends on the nature of the task, the volume of fluid to be administered or withdrawn, and the specific requirements of the procedure. For instance, insulin syringes are designed for precise, small-volume injections, whereas larger syringes are used for drawing blood or administering larger doses of medication.
Adhering to best practices for handling medical syringes is essential to prevent complications such as infections and needle-stick injuries. Maintaining sterility is paramount; healthcare providers must ensure that syringes and needles are used in a sterile environment and that they remain uncontaminated throughout the procedure. Proper injection techniques, such as selecting the correct injection site and angle, can also help minimize patient discomfort and improve the effectiveness of the treatment.
Safe disposal of used syringes is another critical aspect of best practices. Used syringes and needles should be placed in designated sharps containers to prevent needle-stick injuries and contamination. Healthcare facilities must follow local regulations and guidelines for the disposal of medical waste to ensure environmental safety and public health.
Equipping healthcare professionals and caregivers with the knowledge of these best practices ensures that medical syringes are used effectively, responsibly, and safely in their practice, ultimately enhancing patient care and outcomes.